祝贺张瑞平等同学的文章
“Nanoengineered design of inside-heating hot nanoreactor surrounded by cool environment for selective hydrogenations”
被Advanced Materials 接受发表!
Abstract
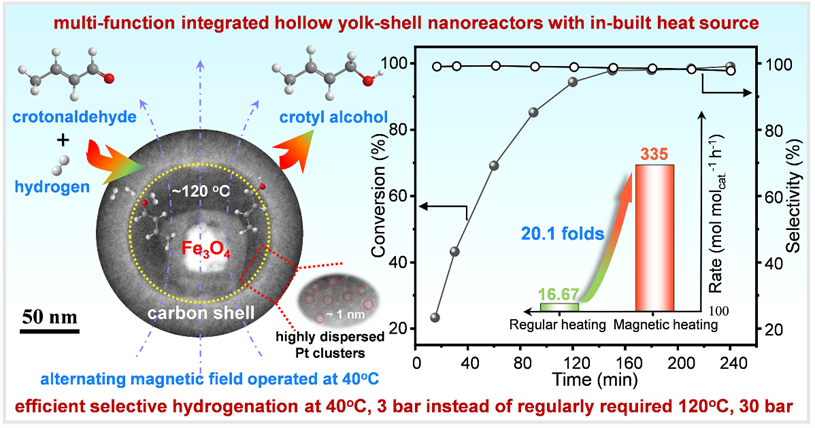
Catalysts with designable intelligent nanostructure may potentially drive the changes of chemical reaction techniques. Herein, we designed a multi-function integrating nanocatalyst, Pt-containing magnetic yolk-shell carbonaceous structure, having catalysis function, microenvironment heating, thermal insulation and elevated pressure into a whole, which induces selective hydrogenation within heating-constrained nanoreactors surrounded by ambient environment. As a demonstration, carbonyl of α, β-unsaturated aldehydes/ketones are selectively hydrogenated to unsaturated alcohols with a >98% selectivity at a nearly complete conversion under mild conditions of 40oC and 3 bar instead of harsh requirements of 120oC and 30 bar. We creatively demonstrate that the locally increased temperature and endogenous pressure (estimated as ~120oC, 9.7 bar) in the nano-sized space greatly facilitates the reaction kinetics under an alternating magnetic field. The outward-diffused products to the “cool environment” retain thermodynamically stable, avoiding the over-hydrogenation often occurs under constantly heated conditions of 120oC. Regulation of the electronic state of Pt by sulfur doping of carbon allows selective chemical adsorption of the -C=O group and consequently leads to selective hydrogenation. It is expected that such a multi-function integrated catalyst provides an ideal platform for precisely operating a variety of organic liquid-phase transformations under mild reaction conditions.

