祝贺颜冬等同学的文章
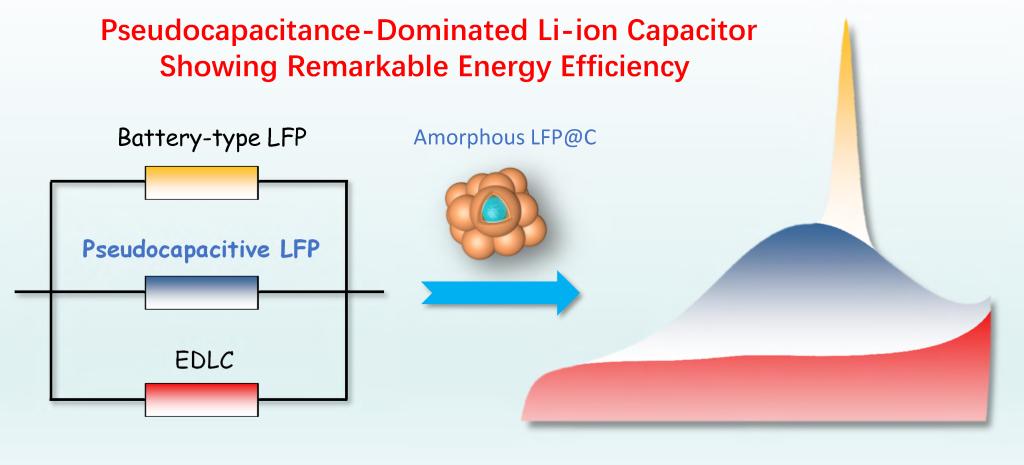
“Pseudocapacitance-Dominated Li-Ion Capacitors Showing Remarkable Energy Efficiency by Introducing
Amorphous LiFePO4 in the Cathode”
被ACS Applied Energy Materials 接受发表!
Dong Yan, An-Hui Lu, Zhi-Yuan Chen, Lei He, Wen-Cui Li*, Pseudocapacitance-Dominated Li-Ion Capacitors Showing Remarkable Energy Efficiency by Introducing Amorphous LiFePO4 in the Cathode. ACS Appl. Energy Mater, 2021, 4, 2, 1824-1832. DOI: 10.1021/acsaem.0c02943 . [DOWNLOAD]
ABSTRACT
Li-ion capacitors (LICs) can be endowed with a satisfying energy density by introducing battery materials in the system, but the polarization of bulk-phase Li insertion, especially from phase transition, sacrifices the crucial energy efficiency at high-power delivery. We herein report the fabrication of a pseudocapacitance-dominated LIC showing advanced energy efficiency and rate capability. The key solution relies on the selective use of nanosized and amorphous LiFePO4 as a cathode, which exhibits pseudocapacitive Li insertion by a solid solution reaction mechanism, thus bypassing the undesired severe phase transition and sluggish ion diffusion in crystalline LiFePO4. After having matched with a highly amorphous carbon anode, the constructed pseudocapacitance-dominated LIC exhibits an excellent energy efficiency of 89% at a maximum energy density of 131 Wh kg−1 . Even ultrafast charging at 25 000 W kg−1 (within 11 s), the energy density can still maintain up to 92 Wh kg−1 without the concession of energy efficiency, which is 62% higher than the conventional configuration based on an adsorption-type activated carbon cathode. This demonstrates the broad potential of the designed pseudocapacitance based on an amorphous structure for integrating energy density and energy efficiency in a power-type device like LIC.

