祝贺高新芊等同学的文章
“Anti-coke behavior of an alumina nanosheet supported Pt–Sn catalyst for isobutane dehydrogenation”
被 Catalysis Science & Technology 接受发表!
Xin-Qian Gao, Wei Song, Wen-Cui Li and An-Hui Lu *. Anti-coke behavior of an alumina nanosheet supported Pt–Sn catalyst for isobutane dehydrogenation. Catalysis Science & Technology, 2021, Accepted. DOI: 10.1039/d0cy02154g. [DOWNLOAD]
Highlight
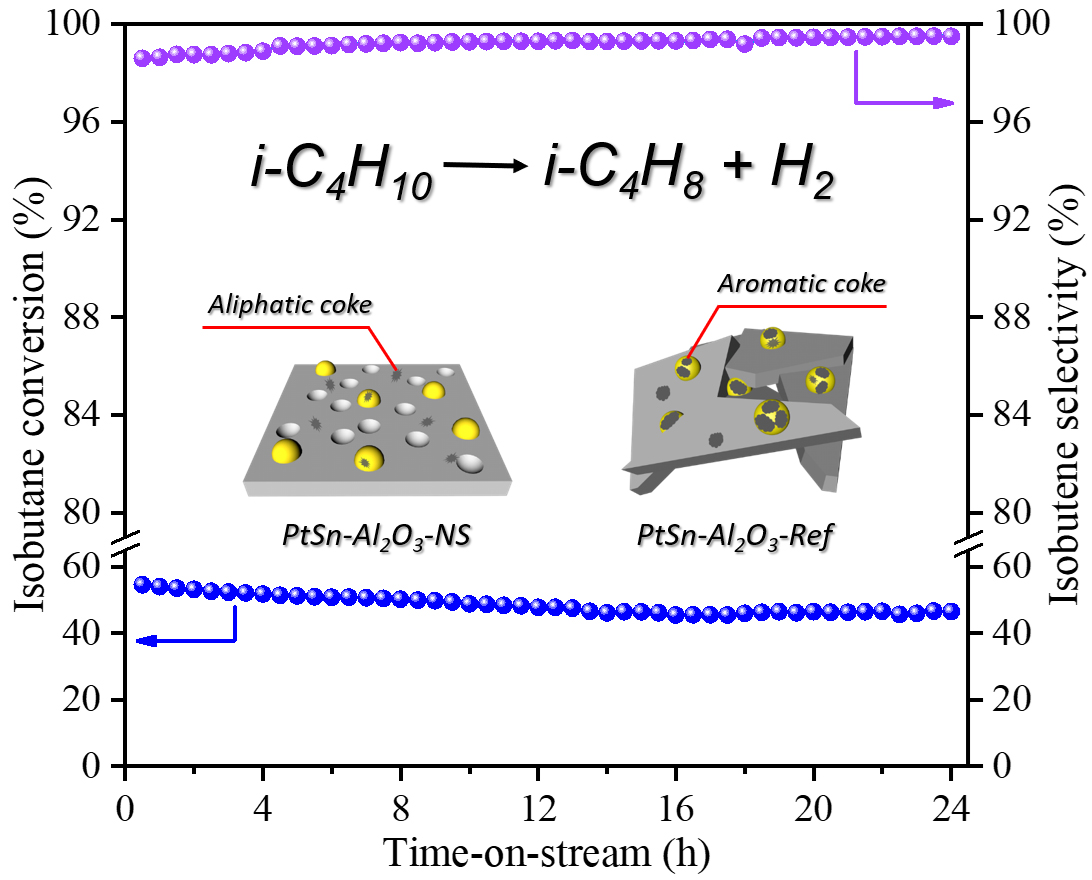
1.The PtSn-Al2O3 nanosheet catalyst showed excellent catalytic performance. The isobutene formation rate was 23.0 mol g Pt-1 h-1 with low deactivation rate of 0.0135 h-1, whereas those value for the reference catalyst were 15.1 mol g Pt-1 h-1 and 0.0303 h-1, respectively.
2.The self-made alumina nanosheets containing abundant unsaturated coordinate Al3+ sites promoted the electronic interactions between platinum and tin, and the lower acidity of corresponding catalyst could inhibit the side reactions and coke formation.
3.The detailed characterization confirmed that coke species were mainly located on the surface of the nanosheets alumina instead of on the metal particles or in the vicinity of the metal particles, ensuring a good exposure of active sites. And the coke species contained more aliphatics with higher disorder degree, facilitating the elimination of coke during regeneration process.
Abstract
In heterogeneous catalysis, carbon deposition on catalysts under the operating conditions is a fatal problem, especially using widely adopted acidic alumina as support. Design of anti-coke catalyst is highly desirable but always remains challenging with the aim of improving the coke tolerance and achieving high catalytic reactivity. Here, we reported an excellent anti-coke capacity of home-made alumina nanosheets supported Pt-Sn catalyst for isobutane dehydrogenation. The prepared alumina nanosheets showed abundant defect sites and less acidity compared to the commercial product. The results of CO-DRIFT spectra showed that the electron density of platinum was further increased with the stronger electronic interactions between platinum and tin on nanosheets alumina. The alumina nanosheets supported Pt-Sn catalyst showed an improved stability, selectivity and activity compared to those well-studied alumina supported Pt-based catalysts in literature, under the dehydrogenation of isobutane reaction conditions of over 24 h at 560 ℃. The detailed characterization confirmed that coke species were mainly located on the surface of the nanosheets alumina instead of on the metal particles or in the vicinity of the metal particles, ensuring a good exposure of active sites. The coke species contained more aliphatics with higher disorder degree, facilitating the elimination of coke during regeneration process. This study demonstrated that a rational design of support structure could be an efficient strategy to govern the coke behaviors of supported catalysts, and thus provide guidelines for the future catalyst design with high reactivity and stability for a variety of catalytic applications.

