High-entropy-driven solvation engineering for sodium ion full cell
Abstract
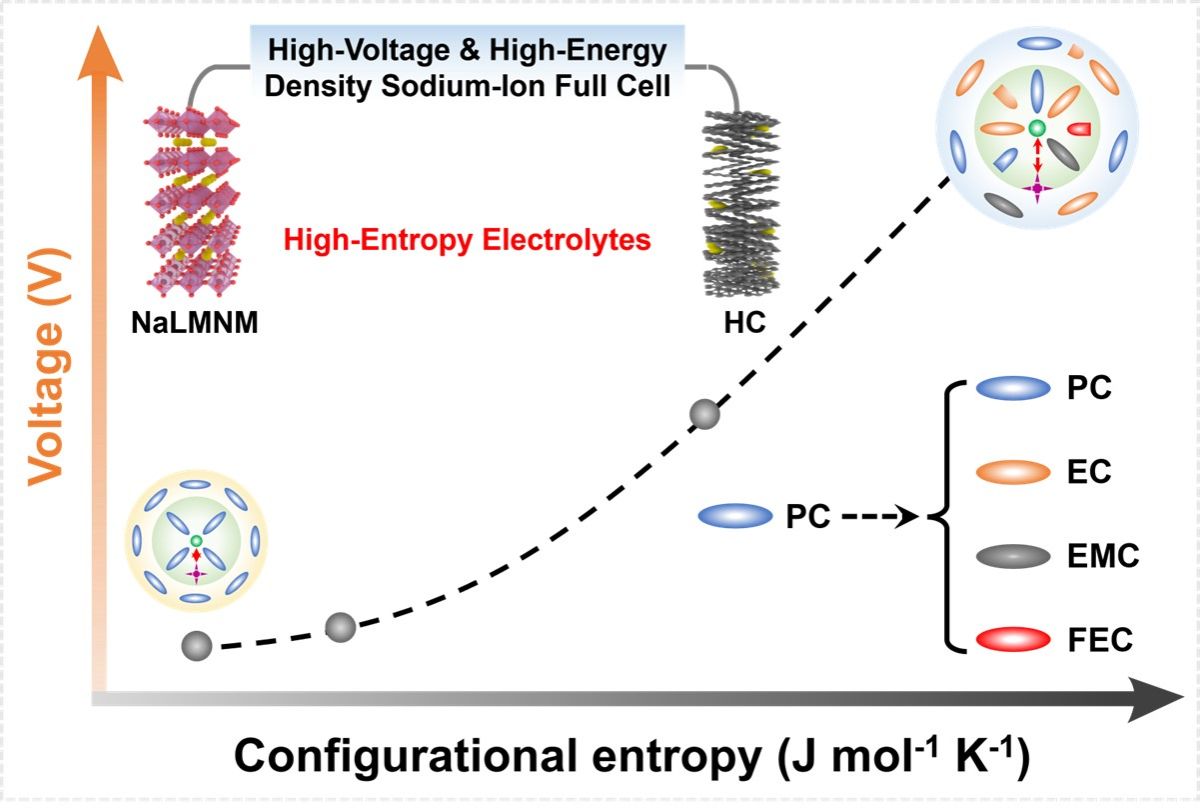
Designing electrolytes compatible with hard carbon (HC) anodes that withstand a wider voltage window remains a challenge in sodium-ion batteries (SIBs). Herein, we develop high-entropy electrolytes by taking a propylene carbonate-based electrolyte as a paradigm, in which various solvents were deliberately introduced to tune the entropy of the electrolyte solvation structure. The formulated high-entropy electrolytes can withstand a voltage of 4.35 V, enabling the Na0.75Li0.15Mg0.05Ni0.1Mn0.7O2||HC full cell to deliver a specific capacity of 114.8 mAh g-1 and to exhibit enhanced rate capabilities and cycling performance. In particular, the cell achieves an energy density of 361.1 Wh kgcathode-1 while preserving a capacity retention of 89.2% after 500 cycles without any presodiation treatment. We not only evaluated the individual roles of each electrolyte component to validate the strategy but also characterized the evolution of the electrolyte-electrode interphase in different electrolytes to elucidate the improved battery performance.

