Achieving high formation rate of C4+ olefins through ethanol upgrading over ZnO/TiO2 catalyst without external hydrogen supply
Abstract
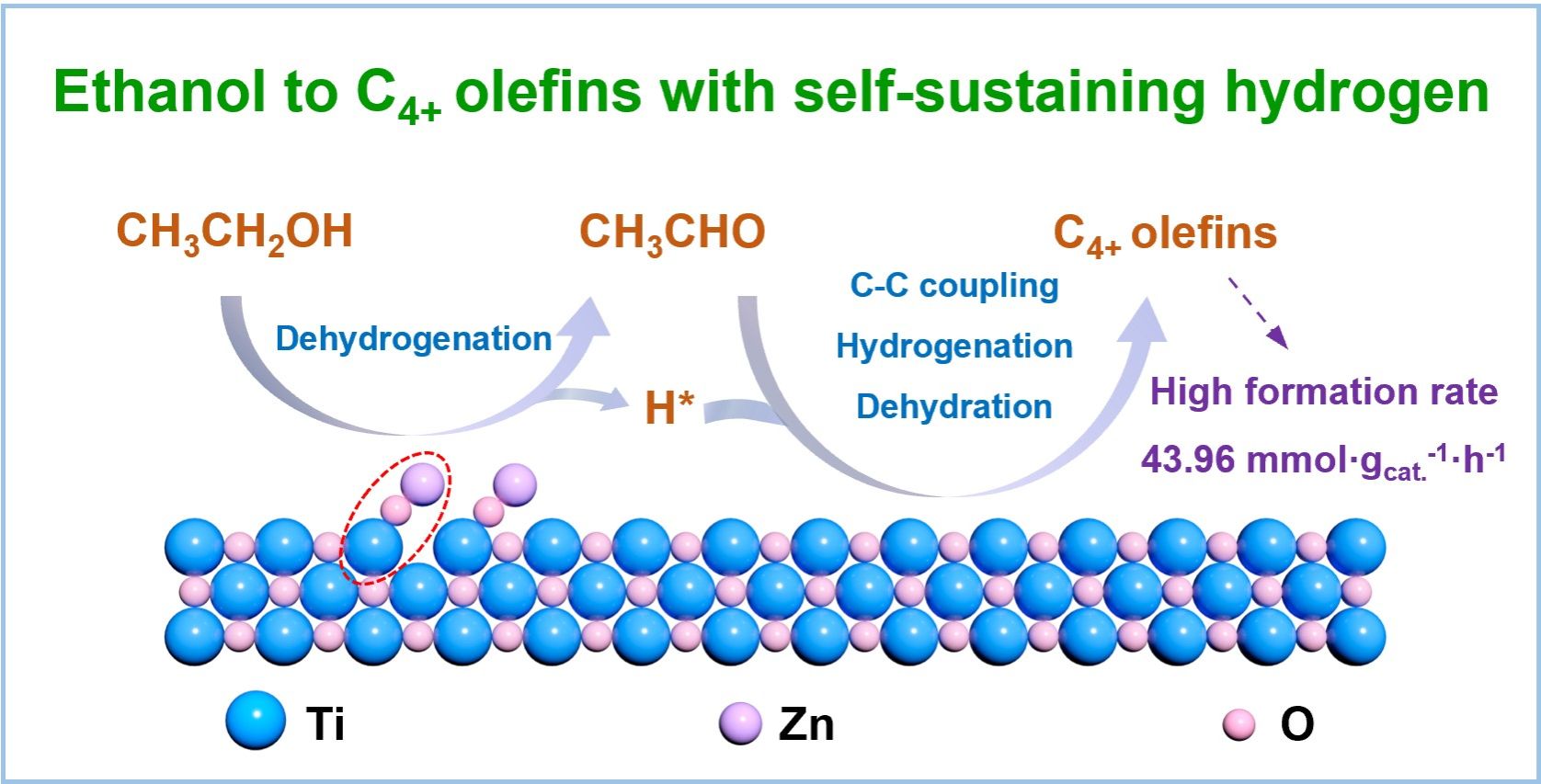
To efficiently convert ethanol into C4+ olefins without an external hydrogen supply, this study designed an anatase-supported zinc oxide catalyst (ZnO/TiO2-A). Combining characterizations with kinetics measurements, we infer that the highly dispersed Zn-O-Ti sites efficiently promote ethanol dehydrogenation to acetaldehyde, which is identified as the rate-limiting step. Concurrently, Ti-O sites with strong C-C coupling ability convert acetaldehyde into high-carbon enal intermediates, which subsequently undergo hydrogenation and dehydration to yield C4+ olefins with a high formation rate of 43.96 mmolC-atom·gcat.-1·h-1, outperforming most reported catalysts in the literature. Crucially, nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy analysis confirms that ethanol acts as an intrinsic hydrogen donor, supplying active hydrogen for the hydrogenation of C=C and C=O bonds in enal intermediates, thereby obviating the need for external hydrogen. This work presents a new strategy employing a non-precious metal oxide catalytic system for upgrading ethanol to high-value products.

